Стратегія керування електроприводом вентильно-індукторного двигуна з покращеними характеристиками
Основний зміст сторінки статті
Анотація
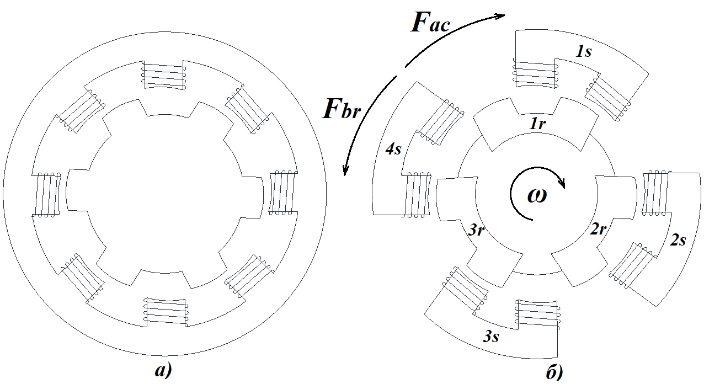
Вентильно-індукторний двигун завдяки своїм перевагам може використовуватися в транспортних засобах низької й середньої потужності. Проте, на даний момент, через значні пульсації обертового моменту, недостатню питому потужність й складність драйвера він не є популярним. В статті розглянуто структуру вентильно-індукторного двигуна й запропоновано методику формування магнітного потоку для забезпечення постійного моменту. За рахунок високочастотного формування струму полюсів статора габарити двигуна мінімізовано. Для підвищення ефективності роботи двигуна запропоновано двохсекційну структуру полюсів із використанням додаткових обмоток. Для формування струму керування обмотками використано розповсюджений резонансний перетворювач з м’яким перемиканням силових ключів. Як результат, запропонований драйвер складається лише з чотирьох резонансних перетворювачів. Робота вентильно-індукторного двигуна симульована в MATLAB® Simulink®.
Блок інформації про статтю

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Автори, які публікуються у цьому журналі, погоджуються з наступними умовами:- Автори залишають за собою право на авторство своєї роботи та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons Attribution License, котра дозволяє іншим особам вільно розповсюджувати опубліковану роботу з обов'язковим посиланням на авторів оригінальної роботи та першу публікацію роботи у цьому журналі.
- Автори мають право укладати самостійні додаткові угоди щодо неексклюзивного розповсюдження роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом (наприклад, розміщувати роботу в електронному сховищі установи або публікувати у складі монографії), за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію роботи у цьому журналі.
- Політика журналу дозволяє і заохочує розміщення авторами в мережі Інтернет (наприклад, у сховищах установ або на особистих веб-сайтах) рукопису роботи, як до подання цього рукопису до редакції, так і під час його редакційного опрацювання, оскільки це сприяє виникненню продуктивної наукової дискусії та позитивно позначається на оперативності та динаміці цитування опублікованої роботи (див. The Effect of Open Access).
Посилання
M. N. Boukoberine, Z. Zhou, and M. Benbouzid, “A critical review on unmanned aerial vehicles power supply and energy management: Solutions, strategies, and prospects,” Appl. Energy, vol. 255, p. 113823, Dec. 2019, DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.113823.
K. I. Laskaris and A. G. Kladas, “Internal Permanent Magnet Motor Design for Electric Vehicle Drive,” IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., vol. 57, no. 1, pp. 138–145, Jan. 2010, DOI: 10.1109/TIE.2009.2033086.
J. D. Widmer, R. Martin, and M. Kimiabeigi, “Electric vehicle traction motors without rare earth magnets,” Sustain. Mater. Technol., vol. 3, pp. 7–13, Apr. 2015, DOI: 10.1016/j.susmat.2015.02.001.
R. Krishnan, Permanent Magnet Synchronous and Brushless DC Motor Drives. CRC Press, 2017, ISBN: 9781315221489.
A. Chiba and K. Kiyota, “Review of research and development of switched reluctance motor for hybrid electrical vehicle,” in 2015 IEEE Workshop on Electrical Machines Design, Control and Diagnosis (WEMDCD), 2015, pp. 127–131, DOI: 10.1109/WEMDCD.2015.7194520.
C. Jiang, K. T. Chau, C. Liu, and W. Han, “Design and Analysis of Wireless Switched Reluctance Motor Drives,” IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., vol. 66, no. 1, pp. 245–254, Jan. 2019, DOI: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2829684.
G. I. Odnokopylov and I. A. Rozayev, “Fault-tolerant control of switched-reluctance drive in emergency modes,” in 2015 International Siberian Conference on Control and Communications (SIBCON), 2015, pp. 1–6, DOI: 10.1109/SIBCON.2015.7147192.
Q. Yu, B. Bilgin, and A. Emadi, “Design considerations of switched reluctance machines with high power density,” in 2016 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), 2016, pp. 1–5, DOI: 10.1109/ITEC.2016.7520226.
S. Sengupta, J. Mukhopadhyay, and S. Choudhuri, “Drive Strategies For Switched Reluctance Motor - A Review,” in Michael Faraday IET International Summit 2015, 2015, DOI: 10.1049/cp.2015.1619.
C.-Y. Ho, J.-C. Wang, K.-W. Hu, and C.-M. Liaw, “Development and Operation Control of a Switched-Reluctance Motor Driven Flywheel,” IEEE Trans. Power Electron., vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 526–537, Jan. 2019, DOI: 10.1109/TPEL.2018.2814790.
X. Deng and B. Mecrow, “Design and comparative evaluation of converter topologies for six-phase switched reluctance motor drives,” J. Eng., vol. 2019, no. 17, pp. 4017–4021, Jun. 2019, DOI: 10.1049/joe.2018.8031.
Y. Hu, T. Wang, and W. Ding, “Performance Evaluation on a Novel Power Converter With Minimum Number of Switches for a Six-Phase Switched Reluctance Motor,” IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., vol. 66, no. 3, pp. 1693–1702, Mar. 2019, DOI: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2840480.
O. Ellabban and H. Abu-Rub, “Switched reluctance motor converter topologies: A review,” in 2014 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), 2014, pp. 840–846, DOI: 10.1109/ICIT.2014.6895009.
X. Deng, B. Mecrow, S. Gadoue, and R. Martin, “A torque ripple minimization method for six-phase switched reluctance motor drives,” in 2016 XXII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), 2016, pp. 955–961, DOI: 10.1109/ICELMACH.2016.7732641.
X. D. Xue, K. W. E. Cheng, and S. L. Ho, “Optimization and Evaluation of Torque-Sharing Functions for Torque Ripple Minimization in Switched Reluctance Motor Drives,” IEEE Trans. Power Electron., vol. 24, no. 9, pp. 2076–2090, Sep. 2009, DOI: 10.1109/TPEL.2009.2019581.
H. Liu, P. C. Loh, X. Wang, Y. Yang, W. Wang, and D. Xu, “Droop Control With Improved Disturbance Adaption for a PV System With Two Power Conversion Stages,” IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., vol. 63, no. 10, pp. 6073–6085, Oct. 2016, DOI: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2580525.
Y. Denisov et al., “Switch operation power losses of quasi-resonant pulse converter with parallel resonant circuit,” in 2016 IEEE 36th International Conference on Electronics and Nanotechnology (ELNANO), 2016, pp. 327–332, DOI: 10.1109/ELNANO.2016.7493078.
I. Verbytskyi, O. Bondarenko, and D. Vinnikov, “Multicell-type current regulator based on Cuk converter for resistance welding,” in 2017 IEEE 58th International Scientific Conference on Power and Electrical Engineering of Riga Technical University (RTUCON), 2017, pp. 1–6, DOI: 10.1109/RTUCON.2017.8124844.
I. Galkin, A. Blinov, I. Verbytskyi, and D. Zinchenko, “Modular Self-Balancing Battery Charger Concept for Cost-Effective Power-Assist Wheelchairs,” Energies, vol. 12, no. 8, p. 1526, Apr. 2019, DOI: 10.3390/en12081526.